In today’s data-driven academic world, standardized testing has evolved from a traditional obstacle into an opportunity for personal and intellectual branding. The Graduation Assessment Test (GAT) is one such challenge—a gatekeeper for postgraduate admissions in many universities, particularly in South Asia.
While the GAT may seem intimidating at first glance, here’s the truth: you don’t need months of study or fancy coaching centers to crack it. With the right tech-enhanced strategies, resourceful tools, and a smart mindset, you can prepare for—and ace—the GAT in a matter of hours.
In this guide, we’ll break down each section of the GAT, share efficient preparation hacks, and highlight tech-powered resources that can turbocharge your results.
Why the GAT Still Matters in 2025
Let’s start with a truth bomb: the GAT isn’t just a test of memory—it’s a test of your logical processing, analytical thinking, and time management under pressure.
Used primarily in Pakistan and administered by NTS (National Testing Service), the GAT is required for admission to M.Phil and MS programs in several universities. Scores also play a role in scholarship selections and even job screening processes in some public and private sectors.
GAT General is composed of three primary sections:
- Verbal Reasoning
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Analytical Reasoning
Each section requires a different approach, and in this post, we’ll explore how to master them efficiently using modern methods and tools.
Step 1: Start With Smart Planning, Not Panic
Before diving into prep, you need to understand the GAT paper structure:
- Verbal Reasoning: 35% weight
- Quantitative Reasoning: 30% weight
- Analytical Reasoning: 35% weight
Once you have this breakdown, allocate your study time proportionally. The idea isn’t to study harder—it’s to study smarter.
Here’s a quick timeline:
- Verbal Reasoning: 2–3 hours
- Quantitative Reasoning: 3–4 hours
- Analytical Reasoning: 3–4 hours
- Practice Tests & Review: 2–3 hours
Yes, that’s roughly 12–14 hours of focused prep, ideally spread over a weekend or two evenings.
Section 1: Mastering Verbal Reasoning
What It Tests:
- Analogies
- Antonyms
- Sentence Completion
- Grammar & Error Correction
- Reading Comprehension
The Tech Approach:
1. Use AI-powered vocabulary apps:
Tools like Magoosh Vocabulary Builder or Quizlet allow you to practice GRE-style words that often pop up in GAT.
2. Take interactive quizzes:
Visit platforms like:
These sites provide categorized questions, so you can drill down into weak areas fast.
3. Read smarter, not harder:
Instead of reading heavy novels, go for editorials in major newspapers like Dawn or The Guardian. Skim them and write quick one-line summaries. This boosts your comprehension speed—crucial for the Reading Comprehension portion.
Pro Tip:
Use browser extensions like Grammarly or LanguageTool to passively learn grammar while browsing or emailing. You’ll sharpen your syntax awareness without even opening a book.
Section 2: Demystifying Quantitative Reasoning
What It Tests:
- Basic Arithmetic
- Algebra & Geometry
- Word Problems (Ages, Work & Time, Profit & Loss)
- Data Interpretation
- Probability & Permutations
The Tech Approach:
1. Start with foundational refreshers:
You don’t need a math degree. Go back to basics using:
- Khan Academy for concept refreshers
- IXL or CK-12 Foundation for practice modules
2. Focused topics for GAT prep include:
- Percentage & Ratio
- Probability
- DMAS (Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction)
- Speed-Distance-Time
- Trigonometry (basic level only)
- Word Problems (Zakat, Profit, Time & Work)
3. Gamify the grind:
Use apps like Photomath or Microsoft Math Solver to scan questions and understand step-by-step solutions.
4. Simulate speed tests:
Set a timer on your phone and try solving 10 questions in 15 minutes. This helps you beat the clock during the real test.
Pro Tip:
Don’t ignore mental math. Apps like Math Workout or MentalUP can help sharpen your brain for quick calculations—no calculator needed!
Section 3: Cracking Analytical Reasoning
What It Tests:
- Pattern Recognition
- Cause & Effect
- Puzzles and Arrangements
- Logical Deduction
- Sequences
The Tech Approach:
1. Think like a coder:
Analytical reasoning is about spotting patterns, much like debugging code. This makes it the perfect section for tech-savvy minds. Platforms like Sheir.org and StudyAndExam.com offer dedicated GAT-style logic puzzles.
2. Play logic games:
Want to build these skills passively? Try logic-heavy games like:
- Elevate
- Lumosity
- Brainwell
- Sudoku or Flow Free
These games build your problem-solving stamina—ideal for those tricky, time-consuming GAT logic puzzles.
3. Practice with actual test samples:
Get real with GAT past papers and simulate test conditions. This helps reduce test anxiety and builds confidence.
Final 3-Hour Power Plan Before Exam Day
Let’s say your GAT is tomorrow—here’s how you can prep efficiently:
Hour 1:
- Quick review of math formulas
- Solve 5–7 math word problems
Hour 2:
- Practice 10 verbal questions from each category
- Skim two reading comprehension passages
Hour 3:
- Solve one full-length analytical section
- Review answers with a solution manual or AI assistant
Bonus: Tech Tools That Make GAT Prep Smarter
| Tool | Use Case |
| Grammarly / Hemingway | Enhances grammar and sentence structure |
| Khan Academy | Math concept clarity |
| Quizlet / Magoosh App | Vocabulary building |
| Photomath / Mathway | Step-by-step math solutions |
| Elevate / Lumosity | Cognitive sharpening & logical thinking |
| Google Sheets | Track your score progress and weak spots |
| Notion or Evernote | Organize revision material efficiently |
SEO Keywords To Target For Organic Growth:
- How to prepare for GAT in one day
- GAT General test preparation tips
- Crack GAT with online tools
- Best apps for GAT preparation
- GAT test strategy 2025
- NTS GAT guide for beginners
- How to study for GAT in 12 hours
Final Thoughts: Tech Your Way to GAT Success
In a hyper-connected world where algorithms can optimize almost anything, why not use tech to optimize your test prep? Cracking the GAT isn’t about rote learning—it’s about smart work, strategic thinking, and making the most of digital tools.
Remember: you already have the knowledge. Now it’s about refining it. Whether you’re applying for grad school, scholarships, or just looking to level up your academic profile, the GAT is your gateway—and you now have the blueprint to pass it like a pro.
If you found this guide helpful, consider sharing it with your fellow GAT warriors or dropping a comment below with your favorite prep strategy!
And hey—don’t forget to bookmark this page for your final review the night before the test.
The preparation of the Graduation Assessment Test (GAT) felt like a cumbersome process. The candidates don’t know, what to read and how to revise concepts to score well in GAT. The admission criteria vary from university to university, but GAT has assigned a major chunk in forming merit. So that GAT plays a vital role in forming the direction of the future.
The preparation of GAT is not about learning anything new, in fact, it is polishing your knowledge. A candidate needs to revise the required concepts in the shortest possible time. Things don’t happen overnight, learning is a steep process; but, with little effort, you can obtain 60-70 marks easily.
First, look for paper distribution, and assign time accordingly.
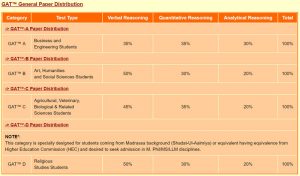
GAT includes three portions Verbal Reasoning, Quantitative Reasoning, and Analytical Reasoning.
Section 1: Verbal Reasoning
- Analogies
- Antonyms
- Sentence Completion
- English Error Correction
- Reading Compression
Verbal Reasoning is solely dependent on your comprehension skills. For GAT-A (General) this section has 35% weigh, which poses 5 types of questions Analogies, antonyms, sentence completion, English error correction, and reading compression.
Links that can be helpful.
https://www.verbalreasoningtest.org/
https://sheir.org/edu/nts/verbal-reasoning/
Section 2: Quantitative Reasoning
Quantitative Reasoning is challenging for a few, but this is the portion where anyone can secure maximum marks. Look for elementary school books such as 7th or 8th standard and thoroughly go through it; above all, it shouldn’t take more than 3 hours. Another way is to search these topics on Google and solve some practice questions.
- Age problem
- Zakat
- Work & Time problem
- Average
- Ratio and proportion
- DMAS
- Permutation
- Median, Mode
- Probability
- Percentage
- Rectangle
- Trigonometry
- Find the value of x?
- Greatest possible value and smallest possible value
- Angle and clock
- Circle
- Product of two numbers
- Speed and distance
- Profit and loss
- Triangle
- General questions
Section 3: Analytical Reasoning
Definition:
“Analytical reasoning refers to the ability to look at information, be it qualitative or quantitative in nature, and discern patterns within the information.” –Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analytic_reasoning
Analytical skills are essential in all fields of life. Practice makes a man perfect. The more you solve the test questions, the more chances are to succeed in the test.
https://sheir.org/edu/nts/analytical-reasoning/
https://www.studyandexam.com/nts-sample-paper4.html
In short, hard work is necessary to secure well in the Graduation Assessment Test (GAT).
